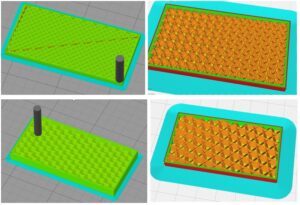
How to create 3D models
While there are a number of ways to create 3D models, most of them boil down to two basic methods: building a model in 3D modeling software, or taking an object from the real world and turning it into a digital model using a 3D scanner. Let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of both methods, and learn how to determine which method is best suited for your task.
Method 1: 3D modeling
The first way to create 3D models is to start from scratch using specialized 3D modeling software. This method is widely used by professionals across various industries: engineers, industrial designers, architects, CGI artists, and many others.
What’s great about this method is that it allows you to design something that doesn’t yet exist – something completely unique like a new component for a car or a fantasy creature in a video game – or something that already exists but is not available for scanning.
For example, if you need a model of a world-famous building located remotely or far from where you are, it can be much easier and more cost-effective to create a 3D model from scratch, using reference materials such as photos and videos, rather than traveling to that place and arranging a 3D scan (which could be a challenge in itself when it comes to historical buildings!). Or, if you need to design something completely new that hasn’t yet been created, 3D modeling is the perfect way to let your imagination run wild and bring your ideas to life.
There are different 3D modeling techniques and different modeling software where you can design a model from scratch. It all depends on the particular object you want to create, and its intended application.
Parametric modeling
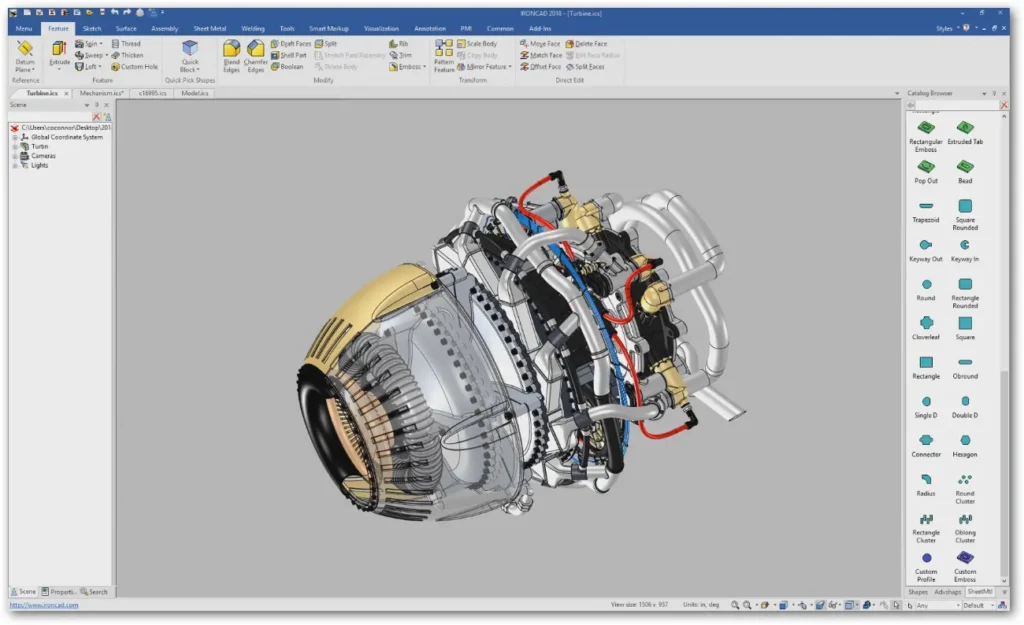
Parametric 3D modeling or CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is the No. 1 method used by engineers and designers to build realistic computer models of future parts and assemblies. Nearly every modern-day product we interact with on a daily basis was created using 3D CAD modeling.
With this method, a designer creates a 3D model of an object that can have all of the same parameters as an actual physical object: material, weight, size, optical parameters, physical parameters, etc. These models can be then 3D printed or CNC machined, as well as used to run complex simulations. For example, you can create assemblies of parts to see how they fit together, test how they will react to forces applied to them, monitor how fluids will flow through them, evaluate how they will be manufactured using simulations, and more.
Given the labor intensity of this method, it is used only for scientific purposes, in production, and in some professional collections of 3D models. For instance, this method was used to create and update the 3DModels.org library.
Polygonal modeling
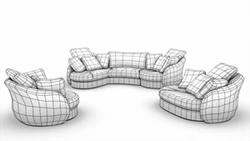
This modeling technique is at the heart of almost every video game or sci-fi movie you have ever seen or played. A polygonal model is built of polygons: flat, two-dimensional shapes, triangles, or quads which the artist is modifying to build a 3D mesh. Unlike CAD modeling, this technique is more concept-driven rather than measurement-driven. Animation and video game studios use polygonal modeling to design everything from movie and game characters to various 3D assets such as weapons, armor, vehicles and entire virtual worlds.
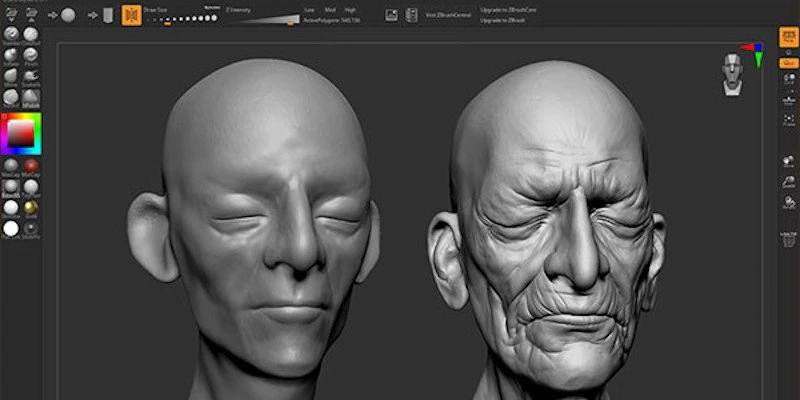
Digital sculpting
|