A Comprehensive Guide for Injection Molding
This article is a comprehensive guide to help you understand the injection molding process, design, material performance, and methods to save cost. It takes around 6 minutes for reading.
Content
- What is injection molding?
- How does injection molding work?
- Injection molding process
- Types of injection molding
- Materials & performance
- When should I choose injection molding?
- Challenges, design tips, and how to save the cost?

What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process during which heated material, such as rubber or plastic, is injected into a mold. It is a cost-effective way to quickly mass-produce parts for a wide variety of industries and applications.
For high-volume plastics manufacturing, injection molding is the best choice as injection molding service makes it cos-effective, consistent quality.
Injection molding also has the widest variety of materials, colors, and configurations compared to CNC machining or even 3D Printing. Beyond materials, injection molded parts can have custom cosmetics, polishes, or surface textures.
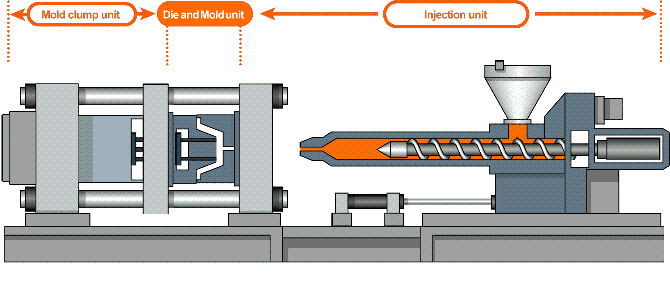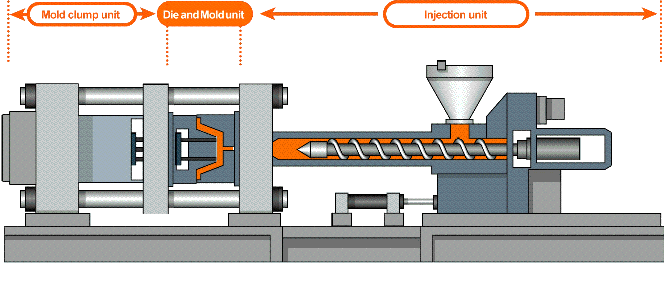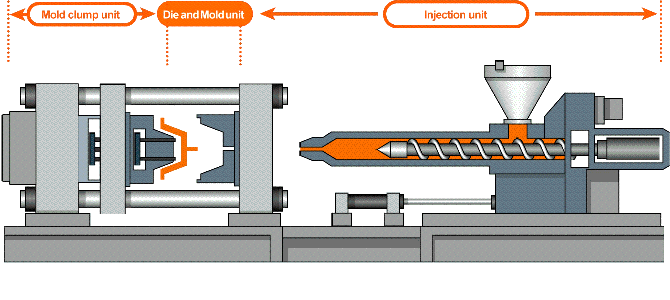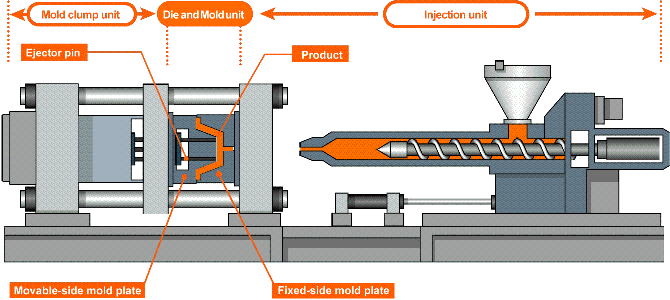
How does injection molding work?
The plastic injection molding process at IN3DTEC is resin pellets are loaded into a barrel where they will eventually be melted, compressed, and injected into the mold’s runner system.
Hot resin is shot into the mold cavity through the gates and the part is molded. Ejector pins facilitate the removal of the part from the mold where it falls into a loading bin.
When the run is complete, parts (or the initial sample run) are boxed and shipped shortly thereafter.
The injection molding process
- The mold closes
- Injection of the heated plastics into the mold
- Mold cooling
- Mold open, parts removing
- Cut the runner & packing

Types of injection molding
- Rapid tooling
Rapid Tooling is a fast and cost-effective process to create aluminum or steel injection molds for quick-turn injection molding. It decreases the time and cost of the product.
- Over-molding
Overmolding is a unique injection molding process that combines two or more components together.
- Insert Molding
Insert molding involves placing an insert or substrate into the mold cavity before injecting it with molten plastic. The insert can be made of metal or any other material that can withstand the temperature and pressure.
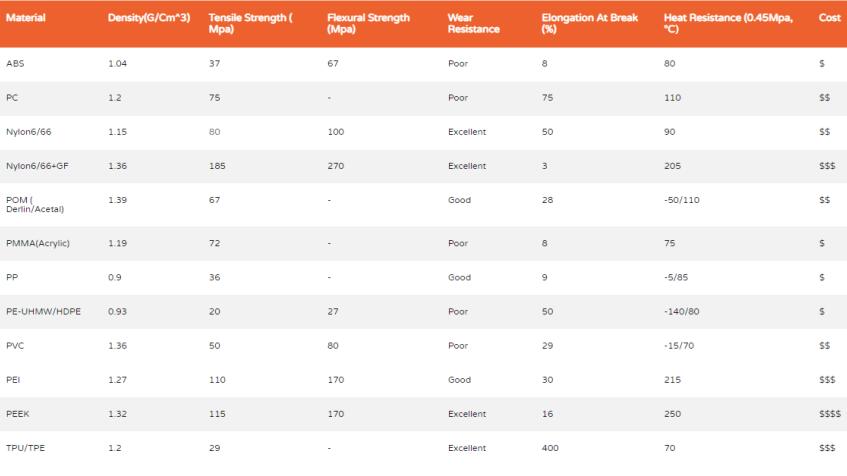
Materials & performance of injection molding
IN3DTEC has more than 50+ plastics for the customer to choose including the common ones: ABS, PC, PC-ABS, PC-ABS & Flame retardant, Nylon6/66, Nylon6/66+GF, POM, PP, HDPE, PVC, PET, PEEK, TPE/TPU/Silicone. Click the image to see the higher resolution.
When to select injection molding service?
Once your design is done or almost done, you can select injection molding to make your parts.
Before that, 3D Printing service is a good choice if your product still needs design verification. A vacuum castingservice will be a good choice if you need the prototyping much more functional than 3D Printing.
There is a simple rule for parts bigger than 100x100x100mm
Quantity: Less than 100, choose 3D printing service; 100 <quantity<300, choose vacuum casting service; amount more significant than 300, choose injection molding service.
For parts, smaller than 100x100x100mm, choose 3D Printing or VC if the quantity is less than 500.
Challenges of Adapting Your Part Manufacturing to Injection Molding
- Initial Design Cost, injection molding design is more complex than 3D Printing & machining. You can click HERE to see a FREE design guide from IN3DTEC.
- Tool Design and tooling cost. We have a professional team to offer your tips to save the cost. You also can click HERE to see the tips for reducing the cost.
- Long Lead Times, 4 to 7 weeks, are necessary for building the injection mold. It takes longer if your project is more complex.
Thanks for reading.