Generative Design Simply Explained
Introduction:
Generative design is an innovative approach to advancing computer-aided design for product designers and engineers. They can easily sort out many complex challenges before the production of any product by incorporating generative design technology.
The generative design leverages cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things to solve intricate issues consisting of scale customization, minimizing the weights of components, optimizing performance, and lowering manufacturing costs.
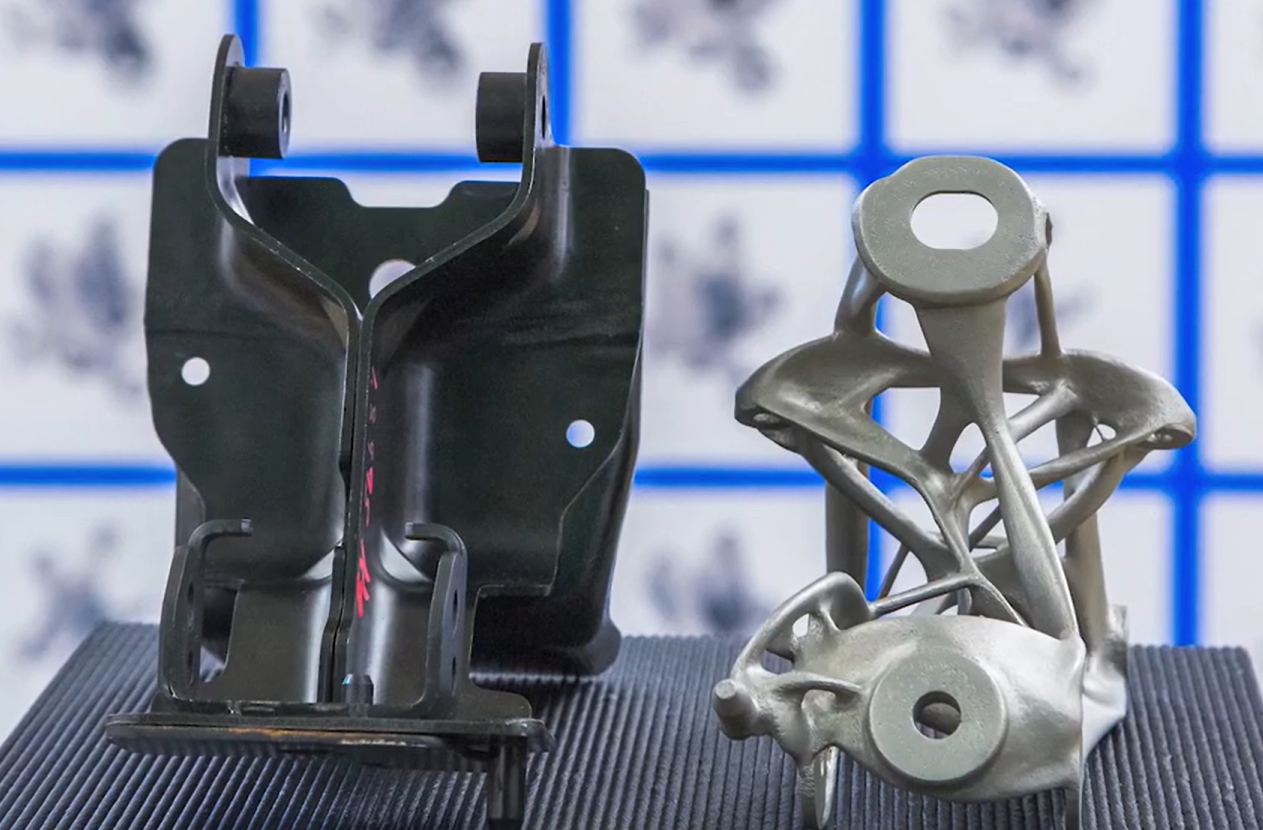
You can say that it is possible to develop a high-performance or robust latticed design with extraordinary features. They are lighter in weight, lower in cost, and more fulfilled with outstanding mechanical properties. Thus, the implementation of generative designs has many practical applications.
In this elaborative article, our main discussion is on what exactly generative design is, its benefits and applications, and how it can help the engineering world.
Brief Explanation of Generative Design
Generative design technology employs AI-driven software and IoT to induce a variety of design part iterations that match a predefined set of parameters given by a product designer.
The conventional modeling procedure starts on the basis of an engineer’s knowledge and sets constraints, whereas generative design needs design parameters, and using them, it harnesses AI to produce a wide number of design solutions.
The best feature of the generative design phenomenon is that it allows product designers to change design parameters by using refined feedback loops.
It lets design engineers identify extremely optimized and customized design solutions for sorting out a huge number of engineering challenges, such as making 3D Printing or CNC machining components lighter, durable, rigid, and economical.
Topology Optimization Vs Generative Design
Topology optimization and generative design are both buzzwords in the manufacturing world. Some people understand that both are the same phenomenon, but in real terms, they are wrong. See how?
Topology optimization begins with a human-designed CAD model to verify its capabilities by applying loads and constraints while keeping project parameters in mind. Then, the topology CAD software will optimize and streamline the model based on the analyzed parameters, while maintaining the mechanical performance of the final object unchanged, and deleting unnecessary parts. This achieves cost savings and other objectives.
It enables rapid design exploration and improve development productivity all while flagging opportunities for part consolidation. Engineers can apply manufacturing constraints at the beginning stages of design including materials, extrusion, draw direction, cavity avoidance and overhead angle. In brief, it can generate optimal manufacture-able structures that meet performance objectives with minimum mass or maximum stiffness.
On the other hand, the technique of generative design is completely different from the former. It does not require a CAD design for further processing; instead, only predefined sets of design parameters or constraints are enough to serve your aims. The software will automatically generate optimized 3D models based on pre-defined parameters, greatly reducing the time required for model creation. Just like our bones grow itself.
Generative Design is Prevalent in the Engineering Field
Traditional designs heavily relied on the knowledge and conceptual ideas of design engineers and product designers. Hands-on drawing and modeling were utilized to conceptualize and test iterations.
Their outcomes were fulfilled with many human-corresponding flaws and errors, like dimensional tolerances and inaccuracies.
Design trends have changed nowadays. All industries depend on designing software to make their virtual prototypes. Computer software has become a main requirement for design engineers as they resolve design challenges.
There is no mandatory framework for the engineers to conceptualize ideas; rather, they specify only high-level performance needs and design frameworks for the generative design software to build 3D Printing or CNC machining parts.
The generative design technique lets computers do thinking and conceptualization, and engineers could focus on innovation and high-level problem-solving technologies.
Applications of Generative Design
Generative design has leapfrogged many industries due to its practical applications. Engineers leverage it in everything from aerospace to manufacturing and consumer goods.
This innovative technology gives manufacturers the freedom to make several modifications, including reducing component weights and manufacturing costs, scaling component customization, and optimizing performance. See how it benefits several industries,
1. Automotive
Generative designs enable automotive engineers to minimize the weight of 3D Printing or CNC machining parts, boost weak design areas, decrease production costs via component consolidation, and lessen the time to market for new products.
2. Sports Equipment
Sportswear manufacturers use generative design technology to achieve new levels of product performance while lowering production costs.
3. Aerospace Industry
Generative design innovations help aerospace fabricators build lightweight plane parts, which are very necessary to lessen fuel consumption, avoid fuel emissions, and offer lower costs.
4. Medical Industry
Generative design is transforming the medical industry by enabling the development of innovative, patient-specific solutions that improve treatment outcomes, enhance patient comfort, and optimize the performance of medical devices.
Benefits of Generative Design
Generative design offers numerous benefits across various industries and applications. Some of the key advantages of generative design include:
- Optimal Performance: Generative design algorithms explore a wide range of design possibilities, considering multiple constraints and objectives. This approach often results in highly optimized designs that maximize performance, structural integrity, and efficiency.
- Design Exploration: Generative design enables designers to explore a vast design space and discover innovative solutions that may have been overlooked using traditional design methods. It encourages creativity and fosters out-of-the-box thinking by generating a multitude of design variations.
- Material Efficiency: By leveraging generative design, the amount of material used in a design can be significantly reduced. The algorithm identifies areas where material can be strategically removed or redistributed, resulting in lighter and more resource-efficient structures. This can lead to cost savings, especially in industries where material expenses are significant.
- Customization and Personalization: Generative design can be employed to create highly customized and personalized products. By inputting specific parameters or constraints, the algorithm can generate designs that are tailored to individual needs or preferences. This level of customization can be particularly valuable in industries like healthcare, where personalized medical devices or prosthetics are required.
- Enhanced Manufacturing Feasibility: Generative design takes into account manufacturing constraints and capabilities during the design process. It generates designs that are more feasible to produce, reducing the likelihood of design errors or manufacturing challenges. This can lead to improved manufacturing efficiency, reduced production costs, and enhanced overall quality.
Generative design has the potential to revolutionize the way products are designed and manufactured, offering a range of benefits that can drive innovation, improve performance, and optimize resource utilization across various industries.