The ultimate guide for ULTEM 3D Printing
Introduction:
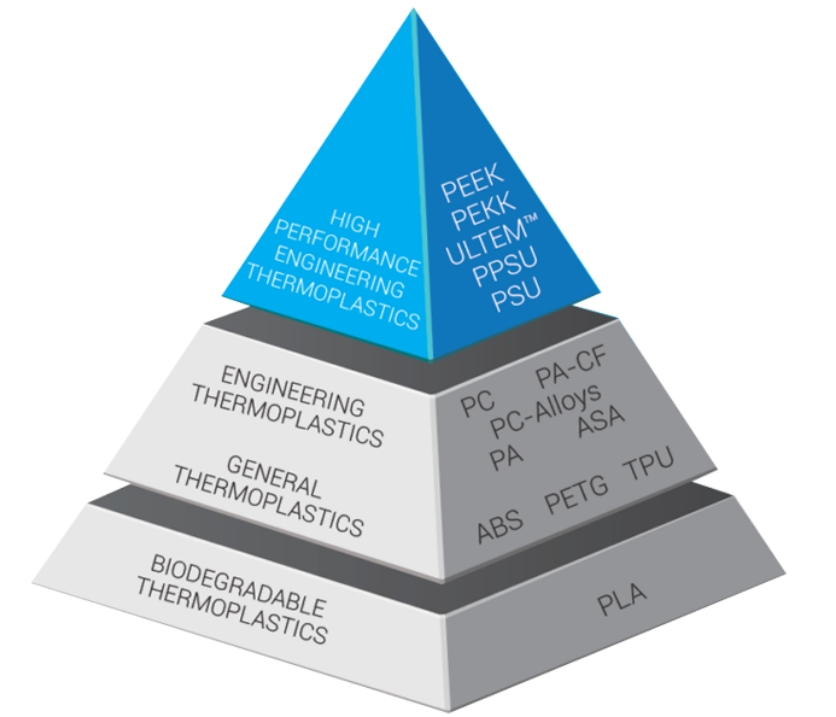
Among the myriad of materials available for 3D printing, ULTEM (also known as PEI or Polyetherimide) stands out as a high-performance thermoplastic that offers exceptional strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. This guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of ULTEM 3D printing, from its properties and applications to the best practices for achieving successful prints.
– What is ULTEM and why is it unique?
ULTEM is part of the family of amorphous thermoplastics, which means it lacks a crystalline structure, resulting in unique mechanical and thermal properties. ULTEM is known for its exceptional strength, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy. It was developed by SABIC Innovative Plastics (formerly General Electric Plastics) and is widely used in various industries for applications that require robust, high-performance materials.
– Different grades and their specific applications of ULTEM.
The grades of ULTEM are typically differentiated by their resin composition, reinforcing additives, and intended use. Here are some commonly used grades of ULTEM:
- ULTEM 1000: This is the standard grade of ULTEM and offers a balance of mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. It has high strength, rigidity, and excellent chemical resistance.
- ULTEM 1010: This grade of ULTEM is specifically formulated for enhanced flow and ease of processing. It offers similar properties to ULTEM 1000 but with improved moldability.
- ULTEM 2300: ULTEM 2300 is a reinforced grade of ULTEM that contains glass fibers for added strength and stiffness. It exhibits excellent mechanical properties, increased dimensional stability, and enhanced creep resistance.
- ULTEM 9085: This grade of ULTEM is specifically designed for additive manufacturing processes, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing. ULTEM 9085 has a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent heat resistance, and meets certain aerospace industry certifications, such as FAA and EASA.
In additional, there are ULTEM 1010CG & ULTEM 9085G which are carbon fiber-reinforced.
ULTEM1010 & 9085 are available in 3D Printing. Others not yet.
Preparing for ULTEM 3D Printing:
– Choosing the right 3D printer for ULTEM.
Because ULTEM printing requires high chamber temperatures, desktop printers are often unable to meet the requirements. When choosing a printer, it is necessary to have at least the following conditions: nozzle temperature capable of reaching 400 degrees Celsius and chamber temperature capable of reaching 150 degrees Celsius (for small-sized prints, 70 degrees Celsius may be sufficient, but the platform must have high-temperature heating capability).
– Essential printer modifications and upgrades.
It is necessary to assess in advance whether printer components such as wiring, mainboards, motors, and others can withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures without combustion or damage, in order to prevent potential disasters. Incidents of printer fires have occurred in the past when printing with high-temperature materials.
– Bed preparation and adhesion techniques.
If your printer platform is a glass bed, it is advisable to acquire a carbon fiber sheet or a disposable ULTEM film. Additionally, it is recommended to use adhesive with PVC content for better adhesion.
– Temperature control and considerations.
Stable temperature is crucial for successful printing, so it is important to monitor nozzle temperature and chamber temperature. Temperature fluctuations are a common cause of printing failures.
ULTEM Printing Parameters:
– Nozzle, Chamber & bed temperature settings: Nozzle 380°C, Chamber 70-200C380°C ( Small size to big size), bed 130-160°C
– Layer height and print speed guidelines: ULTEM1010 better 0.1-0.2mm. Ultem9085 better 0.2mm or more if your printer doesn’t has a nozzle brush.
– Cooling strategies for optimal print quality: No cooling
Designing for ULTEM:You need to consider about the below factors when designing parts for ULTEM
– Design considerations to maximize strength and performance.
– Support structures and their removal techniques.
– Wall thickness and infill recommendations.
– Overhangs, bridging, and interlocking features.
Post-Processing and Finishing:
– Removing support structures and achieving smooth surfaces
Thanks to the easy-off support filament, removing support is not a big problem anymore.
– Sanding, polishing, and other finishing techniques
– Chemical smoothing options
There are some chemicals can help you get better result for ultem prints, such as, Limonene, Acetone, N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF),Methylene chloride. Before attempting any chemical smoothing process, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the safety precautions, ventilation requirements, and specific instructions recommended by the manufacturer of the smoothing agent. It is also advisable to conduct small-scale tests and experiments to determine the optimal process and achieve the desired results.
Applications and Case Studies:
ULTEM (Polyetherimide) is a versatile and high-performance thermoplastic material, and it finds applications in various industries. Here are some common applications of ULTEM:
- Aerospace: ULTEM is used in aerospace applications due to its high strength, lightweight properties, and excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. It is used for components such as interior panels, brackets, electrical connectors, and ducting systems.
- Automotive: ULTEM is utilized in the automotive industry for its high mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to chemicals and heat. It is used in applications like fuel system components, electrical connectors, sensor housings, and under-the-hood parts.
- Electrical and Electronics: ULTEM’s excellent electrical insulation properties make it suitable for electrical and electronic applications. It is used for connectors, sockets, insulators, coil bobbins, switches, and various other components that require high-temperature resistance and electrical performance.
- Medical and Healthcare: ULTEM is used in medical and healthcare applications due to its biocompatibility, sterilizability, and resistance to chemicals. It is used for surgical instruments, medical device housings, orthopedic implants, dental tools, and equipment that require high-temperature sterilization.
- Consumer Products: ULTEM is employed in various consumer products that require high performance and durability. It is used in sports equipment, mobile phone cases, laptop components, appliance parts, and other consumer goods that benefit from ULTEM’s strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance.
- Industrial Equipment: ULTEM is used in industrial applications that require robust and reliable materials. It finds use in pump and valve components, fittings, gaskets, filtration systems, and other equipment that operate in harsh environments or with exposure to chemicals and high temperatures.
Conclusion:
ULTEM 3D printing offers an exciting realm of possibilities for creating durable, high-performance parts and prototypes. By understanding the unique properties of ULTEM, mastering the printing parameters, and implementing best practices, you can unlock its full potential. This guide serves as your go-to resource for navigating the world of ULTEM 3D printing, enabling you to push the boundaries of design, engineering, and innovation.
Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to experiment, learn from your experiences, and enjoy the journey of creating with ULTEM. Happy printing!