Electroplating vs. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Coating: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of surface finishing and coating technologies, Electroplating and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) stand out as two widely adopted methods. Both techniques are essential in enhancing the appearance, durability, and functionality of metal surfaces across various industries. However, they differ significantly in their processes, applications, and benefits. Let’s delve into a comparative analysis of Electroplating and PVD coating.
Electroplating: An Overview
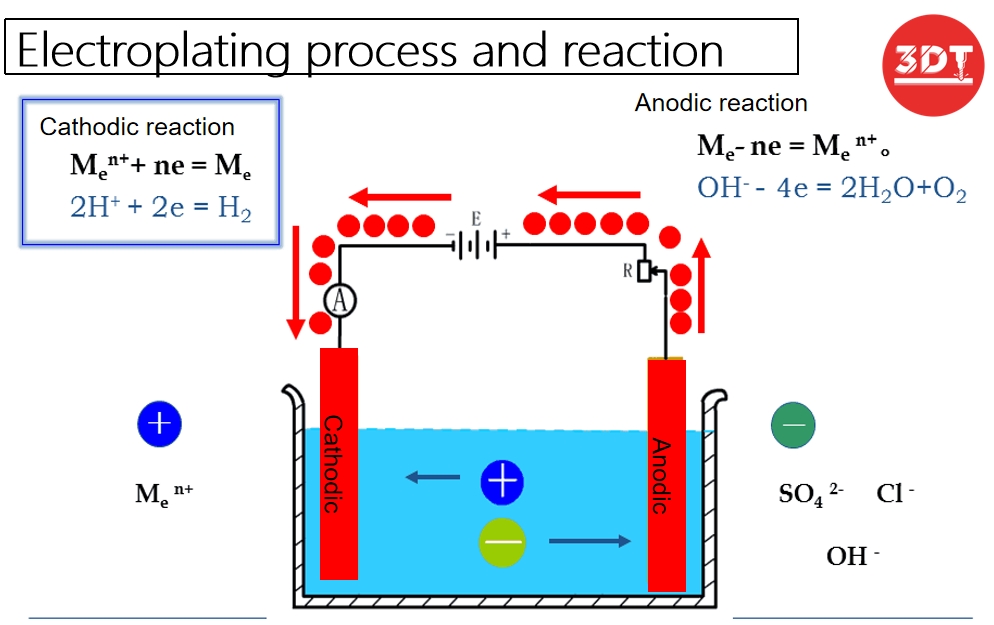
Electroplating is a process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a substrate. This method involves immersing the substrate and a metal anode in an electrolyte solution. When an electric current is applied, metal ions from the anode dissolve and are deposited onto the substrate, forming a coherent metal coating.
Applications of Electroplating:
– Corrosion Resistance:For metals, Electroplating is extensively used to protect metals from corrosion. Commonly plated metals include zinc, nickel, and chromium. For plastics, it can give them a metallic appearance and a mirror-like finish.
– Aesthetic Enhancement: It is often employed to enhance the appearance of items like jewelry, automotive parts, and household fixtures.
– Electrical Conductivity: Electroplating with metals like gold and silver is used in electronics to improve electrical conductivity and solderability.
Several of Projects of electroplating parts by IN3DTEC
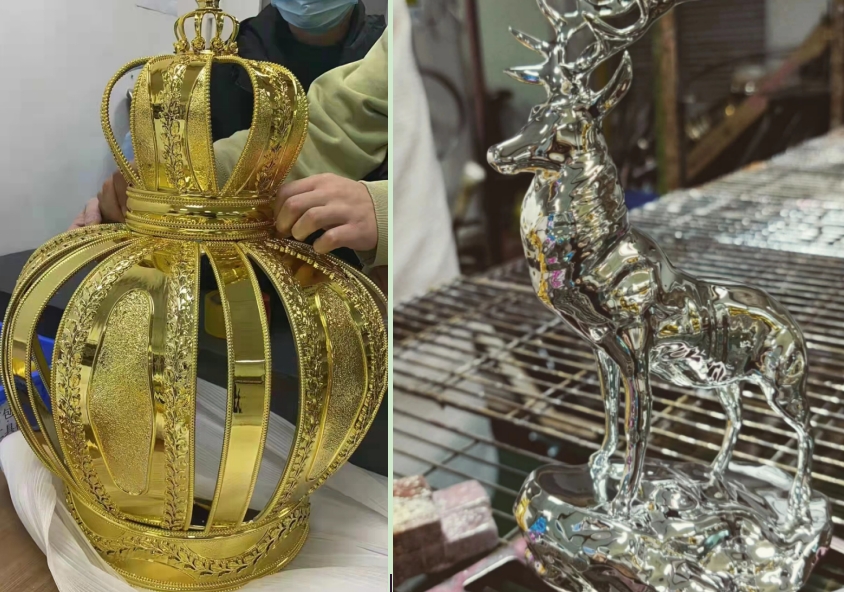
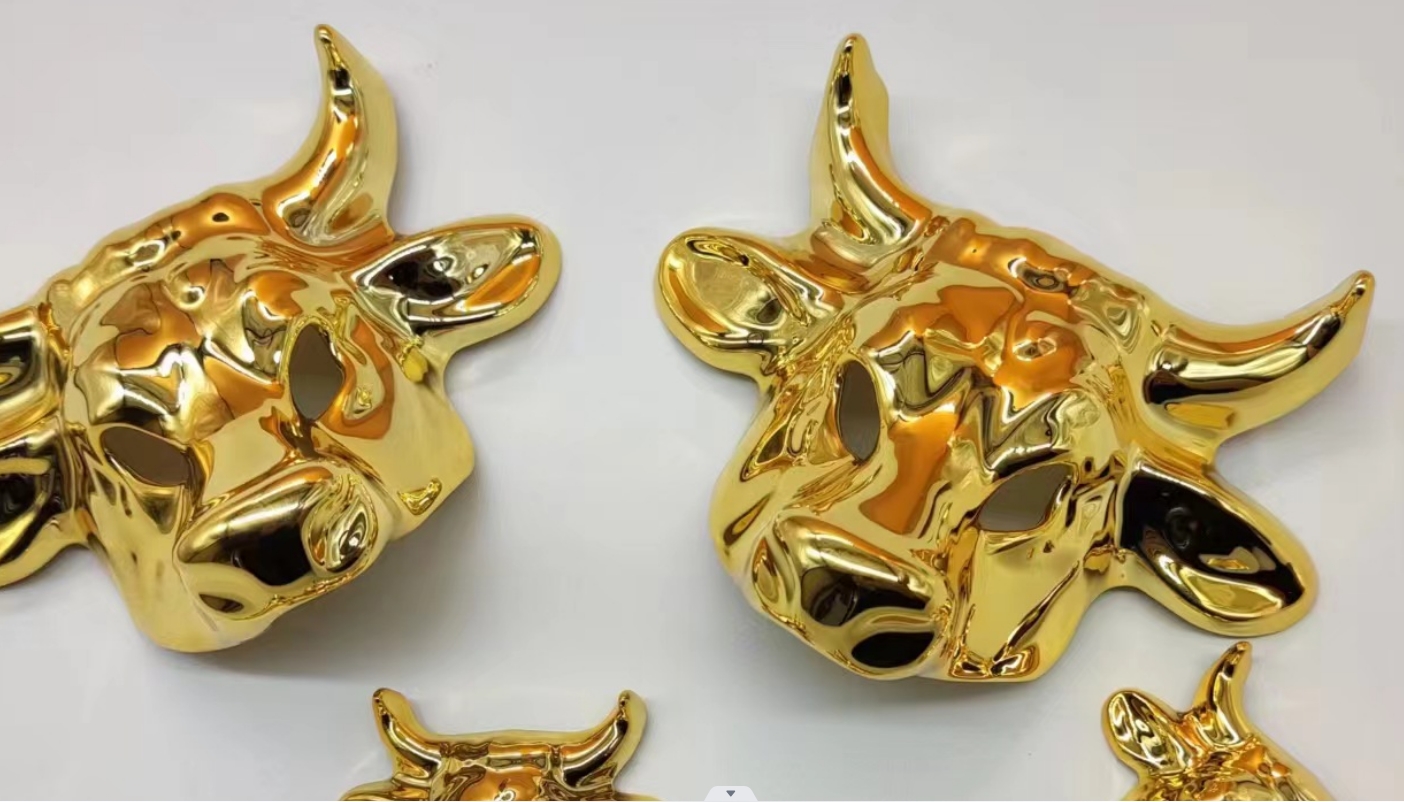
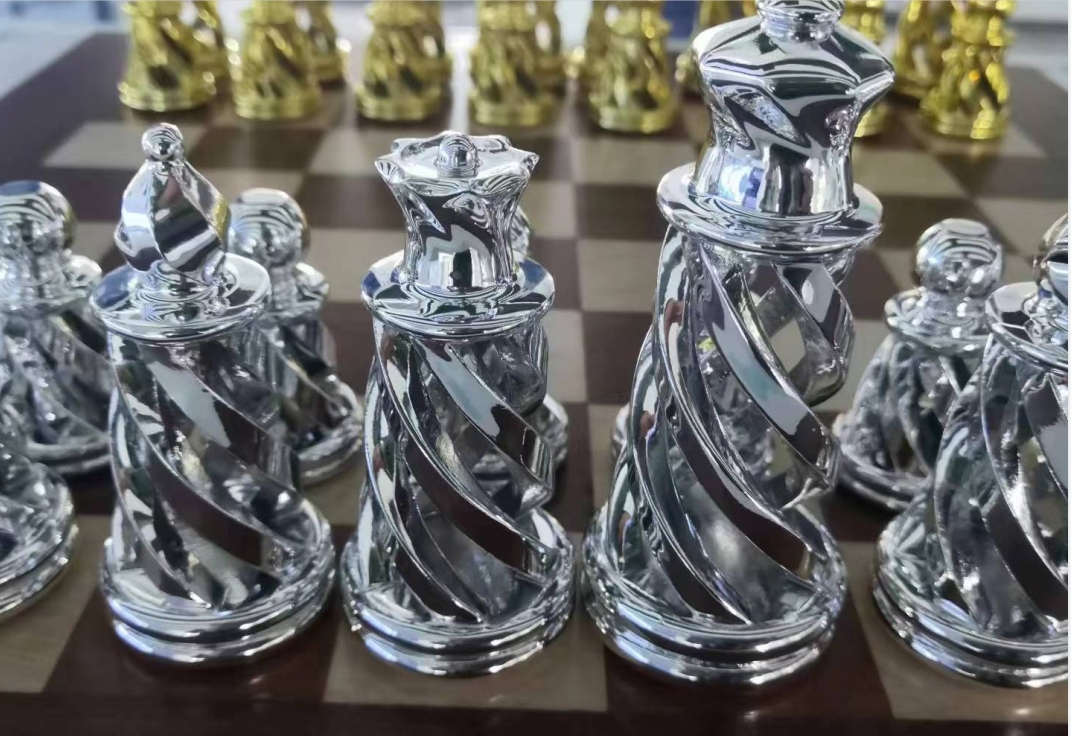
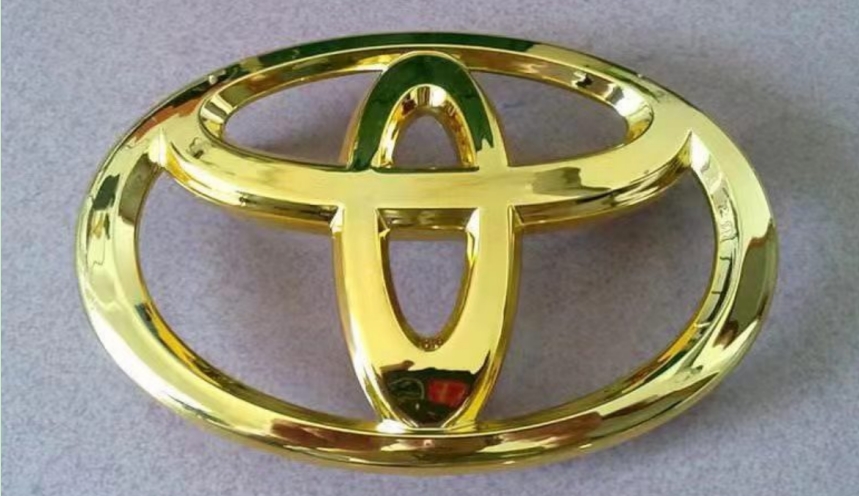




Advantages of Electroplating:
– Cost-Effective: Generally, electroplating is less expensive compared to other coating methods.
– Versatility: It can coat a wide range of metals and alloys.
– Smooth Finishes:The process can produce very smooth and uniform coatings.
Limitations of Electroplating:
– Environmental Impact: The use of toxic chemicals and heavy metals poses significant environmental and health hazards.
– Thickness Limitation: The coating thickness is relatively limited, which might not be sufficient for some applications.
– Adhesion Issues:The bond between the coating and the substrate can be weaker compared to other methods.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Coating: An Overview
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based process where materials are vaporized and then deposited onto a substrate to form a thin film. PVD encompasses various techniques, such as sputtering and evaporation, to achieve the desired coating.
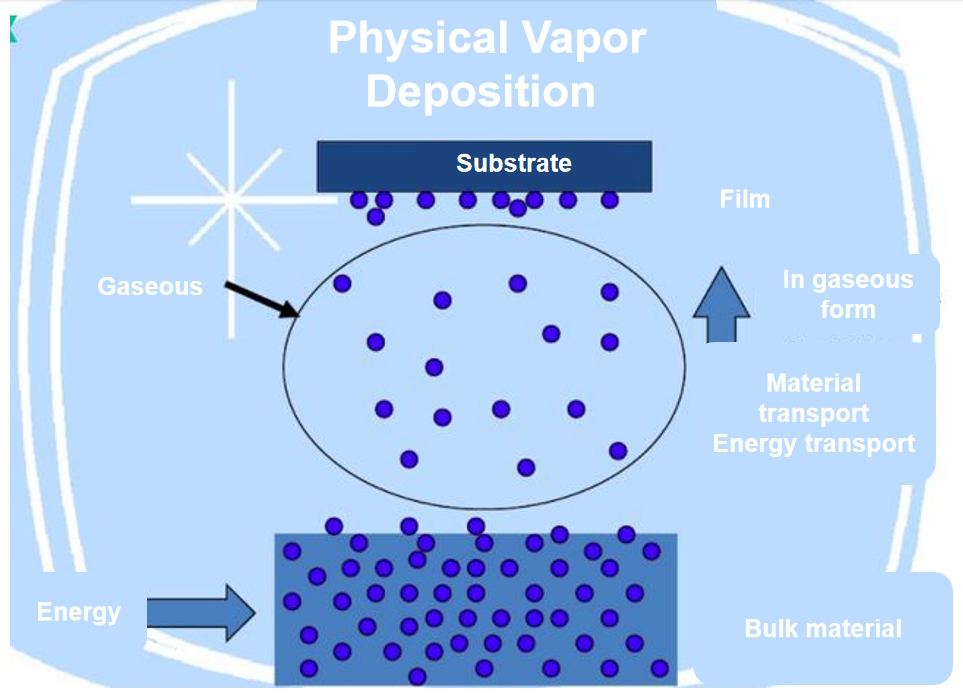
Applications of PVD Coating:
– Tooling and Cutting Instruments: PVD coatings are widely used to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of cutting tools and dies.
– Decorative Finishes: PVD is utilized for providing durable and aesthetically pleasing finishes on consumer goods like watches and electronic devices.
– Protective Coatings: It offers excellent resistance to corrosion and wear, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive components.
Advantages of PVD Coating:
– High Durability:PVD coatings are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance.
– Environmental Friendliness:The process is cleaner and more environmentally friendly compared to electroplating.
– Superior Adhesion: PVD provides excellent adhesion to the substrate, resulting in a long-lasting coating.
Limitations of PVD Coating:
– Higher Costs: PVD coating is generally more expensive due to the complexity of the process and equipment required.
– Process Complexity:The vacuum environment and high temperatures involved can limit the size and shape of the components that can be coated.
– Preparation Requirements: Substrates often require extensive preparation to ensure successful coating adhesion.
Comparative Analysis
- Process and Application:
– Electroplating is a simpler, more cost-effective process suitable for mass production and a variety of metals & plastics. It is ideal for applications where a moderate level of corrosion resistance and aesthetic enhancement are required.
– PVD coating, while more complex and costly, offers superior durability, environmental benefits, and exceptional performance in high-stress applications.
- Environmental and Health Impact:
– Electroplating poses significant environmental and health risks due to the use of hazardous chemicals.
– PVD is a more environmentally friendly option, producing fewer hazardous byproducts.
- Coating Properties:
– Electroplated coatings are generally softer and less durable than PVD coatings.
– PVD coatings provide enhanced hardness, wear resistance, and superior adhesion, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
If your component requires this kind of follow-up treatment, feel free to contact our team for an instant quote, [email protected]
Or find this selection under SLA-Standard ABS-Electroplating from our online store
Conclusion
Choosing between electroplating and PVD coating depends on the specific requirements of the application, including cost, environmental considerations, and the desired properties of the final product. While electroplating offers a cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications, PVD coating provides superior durability and environmental benefits, making it the preferred choice for high-performance and environmentally conscious applications.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method allows for informed decision-making, ensuring the optimal surface finishing solution for various industrial needs.