How to choose the right 3d printing material?
3D printing or additive manufacturing technology, known for its advantages of low-cost and quick turnaround in prototype and on-demand production. It provides product designers and engineers more possibilities when developing new products.
However, because of the rapid changes in 3D printing, the materials it can print also change almost every month. This article aims to help users choose the most suitable 3D printing materials while reducing the cost of use.
Table of contents
It takes around 15 minutes to read
>>The most popular 3D printing technologies & materials
>> Resolution & smoothness
>> Mechanical & chemical performance
>> Surface finishes: coloring, polishing, sand-blasting, anodizing, plating possibilities
>> Special functional materials: flame retardant, waterproof, ESD, medical-grade, flexible materials
>> How to save the 3D Printing cost?
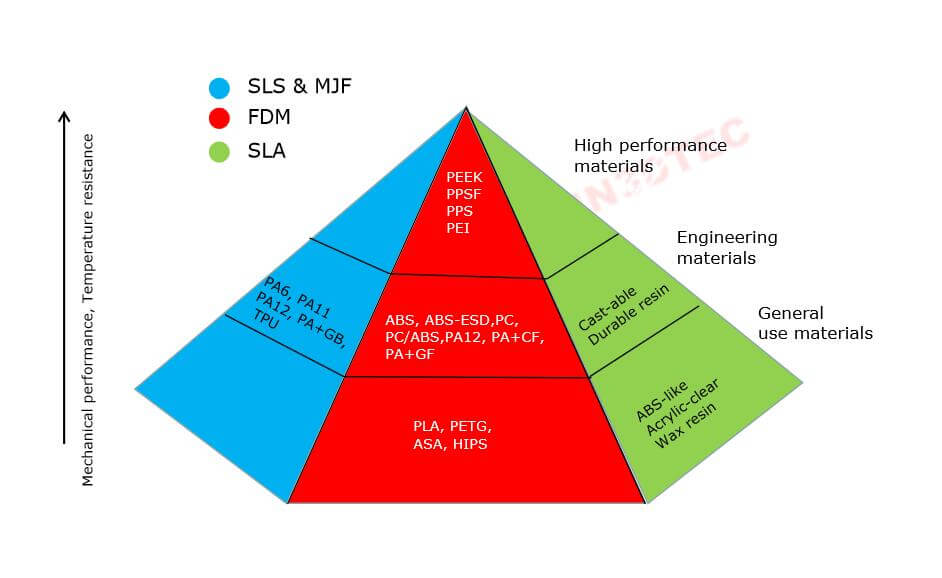
>>The most popular 3D Printing technologies & materials
So far, there are more than 20 types of 3D printing technologies on the market, such as FDM, SLA, DLP, SLS, SLM, EBM, DMLS, CLIP, CJP, Polyjet, and more. However, we only introduce the most commonly used 3D printing technologies & materials here,
FDM( Fused Deposition Modeling)
The process uses a digital design (Gcode) that is uploaded to the 3D printer. The filaments are melted and fed onto the build plate, as the nozzle moves across the build plate, the plastic cools and becomes solid, forming a hard bond with the previous layer, layer by layer until the object is finished.
Stereolithography(SLA)
The SLA 3D Printers begin drawing the layers of the support structures, followed by the object itself, with an ultraviolet laser aimed onto the surface of liquid photopolymer resin. After a layer is imaged on the resin surface, the build platform shifts down and a re-coating bar moves across the platform to apply the next layer of resin. The process is repeated layer by layer until the object is complete.
Selective Laser Sintering(SLS)
The SLS machine begins sintering each layer of part geometry into a heated bed of nylon-based powder. After each layer is fused, a roller moves across the bed to distribute the next layer of powder. The process is repeated layer by layer until the build is complete.
Multi Jet Fusion(MJF)
Multi Jet Fusion uses an inkjet array to selectively apply fusing and detailing agents across a bed of nylon powder, which are then fused by heating elements into a solid layer. After each layer, the powder is distributed on top of the bed and the process repeats until the parts are complete.
Direct metal laser sintering(DMLS, SLM)
The DMLS machine begins sintering each layer-first the support structures to the build plate, then the part itself, with a laser aimed onto a bed of metallic powder. After a cross-section layer or powder is micro-welded, the build plate shifts down and a re-coater blade moves across the platform to deposit the next layer of powder into an inert build chamber. The process is repeated layer by layer until the part is complete.
Parameter | FDM | SLA | SLS | MJF | SLM/DMLS |
Printing principle | Extrusion of melted filament | UV curing | Laser Sintering | Inkjet to selectively apply fusing and agents | Laser Melting |
Layer height | 50-200μm | 25-50μm | 32-50μm | 50-100μm | 50-100μm |
Minimum Wall thickness | 1.0mm | 0.5mm | 0.8mm | 0.8mm | 0.8mm |
Achievable quality | Visible lines on the surface | Very smooth | Smooth | Smooth | Smooth |
>> Resolution & smoothness
Technology | Tolerancing (mm) | Smoothness |
FDM | Length within 100mm +/- 0,25mm; length >100mm, 100*0.25%mm | Visible lines on the surface, Ra24 |
SLS | Length within 100mm +/- 0,2mm; length >100mm, 100*0.2%mm | Smooth, Ra7 |
SLA | Length within 100mm +/- 0,1mm; length >100mm, 100*0.1%mm | Very smooth, Ra4.5 |
MJF | Length within 100mm +/- 0,2mm; length >100mm, 100*0.2%mm | Smooth, Ra7 |
SLM, DMLS | Length within 100mm +/- 0,1mm; length >100mm, 100*0.1%mm | Smooth, Ra7 |
>> Mechanical & Chemical performance
FDM Material-1
Properties | ABS | ASA | PETG | PC | PC/ABS |
Young’s modulus | 2147 | 2379 | 1523 | 2048 | 1832 |
Tensile strength | 33.6 | 43.8 | 31.8 | 62.7 | 39.9 |
Elongation at break | 2.7 | 6.8 | 4.4 | 12.2 | 4.2 |
Bending modulus | 1400 | 3208 | N/A | 2045 | 2081 |
Bending strength | 59 | 73.1 | 55.1 | 94.1 | 66.3 |
Charpy impact strength | 12.6 | 27.5 | 2.4 | 25.1 | 25.8 |
Aceton | dissolve | dissolve | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Water absorption, Equilibrium, 23°C | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Sodium Hypochlorite 15% (Chlorine Bleach) | Slight impact | N/A | N/A | No impact | No impact |
Oil | Slight impact | N/A | N/A | No impact | No impact |
Alcohol, Aliphatic | N/A | No impact | No impact | Slight impact | No impact |
Weathering resistance | Slight impact | No impact | N/A | No impact | Slight impact |
Hot water | Serious impact | Slight Impact | Slight impact | Slight impact | Slight impact |
FDM Material-2
Properties | PA+CF | PEI 1010 | PEI 9085 | PPSF | PEEK |
Young’s modulus | 7453 | 2750 | 2500 | 2100 | 3738 |
Tensile strength | 105 | 68 | 65 | 55 | 98 |
Elongation at break | 3 | 3.3 | 5.8 | 3 | 9.1 |
Bending modulus | 8339 | 3197 | 2550 | 2200 | 3612 |
Bending strength | 169 | 120 | 110 | 110 | 147 |
Charpy impact strength | 13.4 | 30 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Acetone | No impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | N/A | No impact |
Water absorption, Equilibrium, 23°C | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Sodium Hypochlorite 15% (Chlorine Bleach) | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Oil | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Alcohol, Aliphatic | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Weathering resistance | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Hot water | Slight impact | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
SLA Materials
Properties | ABS-like | Acrylic-Clear Resin | Somos-Taurus | Somos-128 | Somos-8000 |
Young’s modulus | 2500 | 2860 | 2310 | 2946 | 2370 |
Tensile strength | 40 | 55 | 46.9 | 56.8 | 47.2 |
Elongation at break | 4 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 8 |
Bending modulus | 2300 | 2410 | 2054 | 2654 | 2222 |
Bending strength | 70 | 82 | 73.8 | 80 | 66.8 |
Charpy impact strength | 10.5 | 10.5 | 47.5 | 38.9 | 23 |
Acetone | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Water absorption, Equilibrium, 23°C | Slight impact | Slight impact | Slight impact | Slight impact | Slight impact |
Sodium Hypochlorite 15% (Chlorine Bleach) | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Oil | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Alcohol, Aliphatic | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Weathering resistance | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact | Serious impact |
Recommended Max. use temperature | 35°C | 35°C | 45°C | 45°C | 45°C |
SLS Materials
Properties | PA6 | PA12 | TPU | PA+GB |
Young’s modulus | 3200 | 1650 | 61 | 3200 |
Tensile strength | 74 | 48 | 18 | 51 |
Elongation at break | 4 | 4 | 276 | 9 |
Bending modulus | 2300 | 1500 | 86 | 2900 |
Bending strength | 99 | N/A | 6.2 | 70 |
Charpy impact strength | 10.5 | 53 | No break | 35 |
Acetone | No impact | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Water absorption, Equilibrium, 23°C | No impact | No impact | Slight impact | No impact |
Sodium Hypochlorite 15% (Chlorine Bleach) | N/A | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Oil | Slight impact | No impact | Slight impact | No impact |
Alcohol, Aliphatic | N/A | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Weathering resistance | No impact | No impact | N/A | No impact |
Hot water | Slight impact | Slight Impact | Slight impact | Slight impact |
MJF Materials
Properties | PA11 | PA12 | PA+GF |
Young’s modulus | 1800 | 1800 | 2500 |
Tensile strength | 52 | 48 | 30 |
Elongation at break | 60 | 20 | 10 |
Bending modulus | 1700 | 1800 | 2700 |
Bending strength | 65 | 70 | 65 |
Charpy impact strength | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Acetone | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Water absorption, Equilibrium, 23°C | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Sodium Hypochlorite 15% (Chlorine Bleach) | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Oil | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Alcohol, Aliphatic | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Weathering resistance | No impact | No impact | No impact |
Hot water | Slight impact | Slight impact | Slight impact |
>> Surface finishes: Coloring, Polishing, Sandblasting, Plating, Anodizing…
Technology | Initial colors | Polish & Coloring | Coloring |
FDM | Multiple colors | Sand-blasting, Sand-paper polish | Spray Painting, Plating |
SLS | White | Sand-blasting | Dyeing & Spray Painting |
SLA | White, Clear, | Sand-paper polish | Spray painting, Plating |
MJF | Grey, Black | Sand-blasting | Dyeing & Spray Painting |
SLM, DMLS | Metal color | Sand-blasting, Electropolishing | Anodizing, Spray Painting, Plating |
>> Special functional materials: flame retardant, UV resistance, ESD, medical-Grade, waterproof
Medical grade Materials:
ABS M30i(FDM), PEEK(FDM), PPSF(FDM), PA12( SLS & MJF), PA11(MJF), Ti64( SLM)
ESD Material:
ESD-ABS
Flame retardant materials:
PC-FR(FDM), PEI 1010 & 9085(FDM), PEEK(FDM), PA12-FR(SLS), PPS(FDM)
Waterproof materials:
PETG(FDM), PC(FDM), PEEK(FDM), PA12+GF(MJF)
UV resistance:
ASA, PC, Nylon+CF, PEEK, PEI
Flexible materials:
TPU95A & 85A(FDM), TPU75A & 90A(SLS), TPU50A(SLA). For high-standard TPU, we recommend using our Vacuum Casting service, please click HERE to learn more.
>>How to save the 3d printing cost?
Compared with CNC, 3D printing is not sensitive to the complexity of the objects. For example, in IN3DTEC’s China factory, one technician can control 15 to 20 devices at the same time. Therefore, the cost of 3D printing mainly depends on the weight of the part, So the most direct way to reduce costs is to make less weight of the objects, below are 4 free tips,
1. Choose the right material
Plastics:
the cost from high to low following by PEEK>PEI 1010=PPSF>PEI9085>PA+GF>PA+CF>PPS>PPA>PA6/66/12>ASA>PC>PC/ABS>ABS>PETG>PLA
Metals:
Ti64>>18Ni300>Stainless>Aluminum
2. Hollow the part
Samples with low strength requirements can be hollowed
3. Reduce the infill percentage(mainly for FDM)
4. Avoid any structure needs much support (Talk to us for any confusions)