Electroplating Metal 3D Prints: A Guide to Enhancing Surface Finishes
When it comes to 3D printing, metal prints already offer exceptional strength, durability, and a professional appearance. However, even metal prints can benefit from a touch of refinement. Electroplating, the process of adding a metallic layer through an electrochemical process, can enhance the surface quality, durability, and functionality of metal 3D prints. But is it possible to electroplate metal prints, and how does it work? Let’s explore this exciting technique.
Why Electroplate Metal 3D Prints?
Even though metal 3D prints are inherently robust, electroplating can further enhance their properties:
- Improved Aesthetics: Achieve a polished, uniform finish or even a different metallic appearance, such as gold or chrome.
- Corrosion Resistance: Add a protective coating that prevents oxidation or environmental damage.
- Increased Durability: Enhance wear resistance for functional parts.
- Electrical Conductivity: Optimize the surface for electronics or conductive applications.
Electroplating is particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and jewelry, where aesthetics and performance go hand in hand.
Understand more about the electroplating process.
Can You Electroplate Metal 3D Prints?
Yes, metal 3D prints can be electroplated, and the process is often more straightforward than plating plastic prints. The primary reason is that metal substrates are typically conductive, eliminating the need for a conductive coating step. However, the success of the electroplating process depends on factors such as the type of metal used in the 3D print and the plating metal.
Commonly used metals in 3D printing, like stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum, are excellent candidates for electroplating.
Electroplating Metal 3D Prints: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Surface Preparation
- Clean the Print: Remove oils, dust, or residue from the surface using isopropyl alcohol or an ultrasonic cleaner.Dry the print 4-5 hours in the oven.
- Smooth the Surface: Sand or polish the part to remove imperfections. A smooth surface ensures a uniform electroplated finish.Try to use tumbling if the parts are more difficult to be manually polished.
Step 2: Apply a Base Layer (If Necessary)
Some metals, like aluminum, require a base layer (e.g., zincate or copper) before electroplating because they don’t adhere well to certain plating solutions.
Step 3: Prepare the Electroplating Setup
- Electroplating Bath: Choose a solution compatible with your desired plating metal (e.g., nickel, copper, or gold).
- Power Supply: Use a DC power supply for controlling the current during the plating process.
- Anode and Cathode Setup: Attach your metal 3D print to the cathode (negative terminal) and use the plating metal as the anode (positive terminal).
Step 4: Electroplate the Metal Print
- Immerse the Print: Submerge the print into the electroplating bath.
- Set the Current: Adjust the current to match the plating solution specifications.
- Monitor the Process: The plating process can take minutes to hours depending on the desired thickness.
Step 5: Post-Plating Finishing
- Rinse: Wash the part in distilled water to remove plating solution residue.
- Polish: Buff the plated surface to achieve the desired shine or texture.
- Seal the Surface: For some metals, apply a protective coating to prevent tarnishing or oxidation.
Tips for Electroplating Success
- Choose Compatible Metals: Not all combinations of substrate and plating metals adhere well. Research compatibility beforehand.
- Avoid Overplating: Excess plating thickness can lead to uneven surfaces or peeling.
- Test Small Parts First: Before electroplating a critical piece, practice on smaller or less important parts.
- Use Proper Safety Measures: Work in a ventilated area and use gloves to handle chemicals safely.
Applications of Electroplated Metal 3D Prints
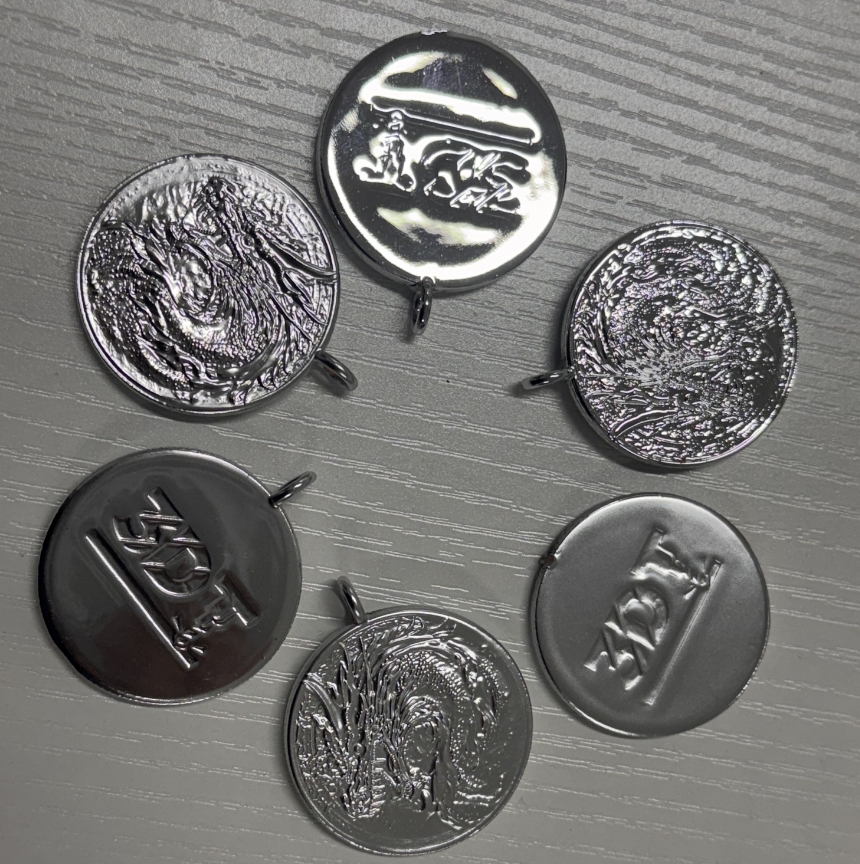
- Jewelry: Enhance the appearance of 3D-printed gold, silver, or platinum pieces.
- Functional Components: Add wear-resistant coatings to industrial parts.
- Decorative Items: Improve the polish and aesthetic appeal of sculptures or consumer products.
Challenges to Consider
- Surface Porosity: Some metal 3D printing techniques (e.g., binder jetting) result in porous surfaces that may require sealing before plating.
- Cost: Electroplating setups and solutions can add to project costs.
- Skill Requirement: Proper preparation and technique are critical for high-quality results.
Need the electroplating finish on your metal 3d prints? Submit your project details, and we will offer you a cheapest and affordable cost for your parts.
Conclusion
Electroplating metal 3D prints is not only possible but also a powerful way to enhance their appearance and functionality. By following the right steps and understanding the compatibility between your print material and plating metal, you can create durable, eye-catching, and professional-quality parts.
Whether you’re producing jewelry, functional prototypes, or decorative items, electroplating is a versatile technique that can elevate your 3D printing projects to the next level.
More article: