CNC Machining Service VS 3D Printing
Select the right technology to save your time and cost
All uploads are secure and confidential
Table of contents
>> Introduction
>> Materials
>> Geometric Complexity Accuracy, Cost, Quality
>> Post-processing
>> How to choose the right technology?
>> Price comparison
>> Introduction
CNC is one of the most popular methods of manufacturing for both small one-off jobs and medium to high volume production. It offers excellent repeatability, high accuracy, and a wide range of materials and surface finishes.
3D printing, involves parts being created layer-by-layer using materials such as plastic filaments (FDM), resins (SLA/DLP/LCD), plastic or metal powders (SLS/DMLS/MJF/SLM). Using a source of energy such as a laser or heated extruder, layers of these materials are solidified to form the finished part. It is becoming a tool for helping designers, product developers to get parts fast and easy.

The key difference between 3D printing and CNC machining is that 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, whilst CNC machining is subtractive. This means CNC machining starts with a block of material (called a blank), and cuts away material to create the finished part. To do this, cutters and spinning tools are used to shape the piece. Additive Manufacturing (AM) or 3D Printing processes build parts by adding material one layer at a time. AM processes require no special tooling or fixtures.
>>CNC & 3D Printing available materials
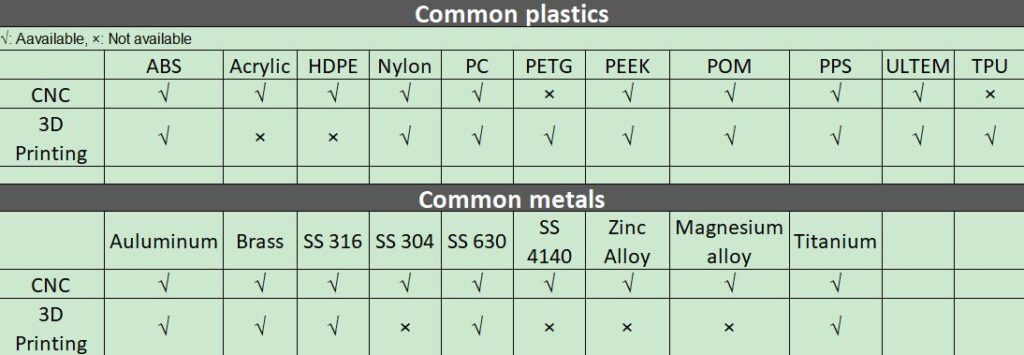
CNC is mainly used for machining metals. It can also be used for machining thermoplastics, acrylics, softwoods and hardwoods, modeling foams and machining wax.
3D Printing is predominately used with plastics and extending to more metals in recent years, it also supports some customized materials, such as PEEK+ Carbon or glass fiber, Cast-able, Flame retardant, ESD materials.
The chart below is a comparison of CNC and 3D printing materials.
>>Geometric Complexity Accuracy,Cost,Quality
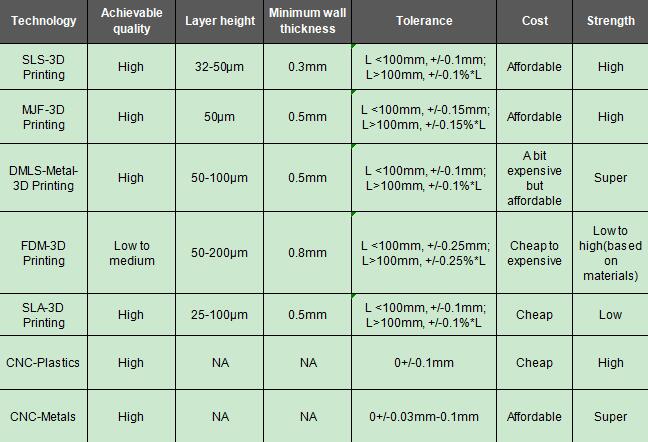
3D printing is well-known for its advantages in creating parts with high geometric complexity. Though CNC can produce complexity part by using 4 or 5 axis CNC systems, it still has some limitations, cause the jigs & fixtures should be customized, some internal channels can’t be reached, very thin walls easily broken by CNC.
3D printing is not sensitive to the complexity of the structure, Allow designers to have unlimited spatial imagination.
Please refer to the table below for a more detailed comparison
>>Post processing
To achieve a improve functionality or aesthetics of the manufactured parts, the users need to know some common post-processing techniques, we are hereby listing some processes below:
CNC: Anodizing, Bead blasting, Nitride, Oxide, Powder coating
3D printing: Dyeing, Painting, Media blasting, Sanding, and hand polish, Metal plating
Please refer to the table below for a more detailed comparison
>>How to Choose the right technology?
High Geometric structure: 3D Printing is better
Dimensional accuracy: CNC is better
Mechanical properties in all 3 dimensions: CNC is better
Lead time: CNC need around 6-8 days, 3D printing can as fast as one day
Cost: 3D printing is generally cheaper than CNC
Resolution: In general CNC is better than 3D Printing
Smoothness: CNC is better
Quantity: In general, Both of CNC and 3D Printing are more suitable for parts under 1000 pieces, which we call them low-volume production
>>Price comparison
For your better vision of the price difference between CNC and 3D Printing, we are hereby taking a sample below as an example:
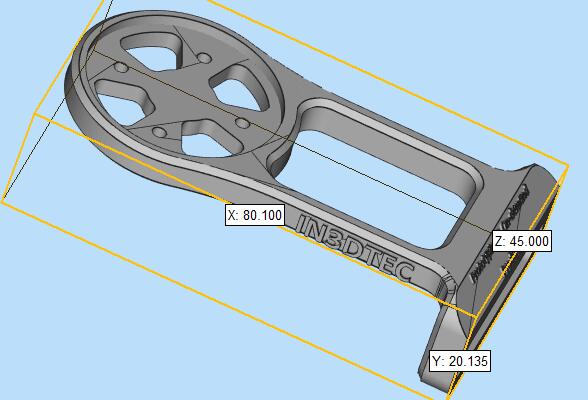
Part name: Bicycle Stopwatch Holder
Volume: 80mm x 45mm x 20mm
File download link: Click HERE
Cost analysis
ABS PC Nylon Aluminum
CNC: $21 $21 $21 $37
3DP: $5 $6 $7 $35
Kind reminder: The price is based on 10 pieces each, there is always a MOQ for each technology. For 3DP(3D printing), ABS & PC are based on FDM, Nylon is based on MJF or SLS, Aluminum is based on DMLS.