How to 3D Print TPU: A Comprehensive Guide
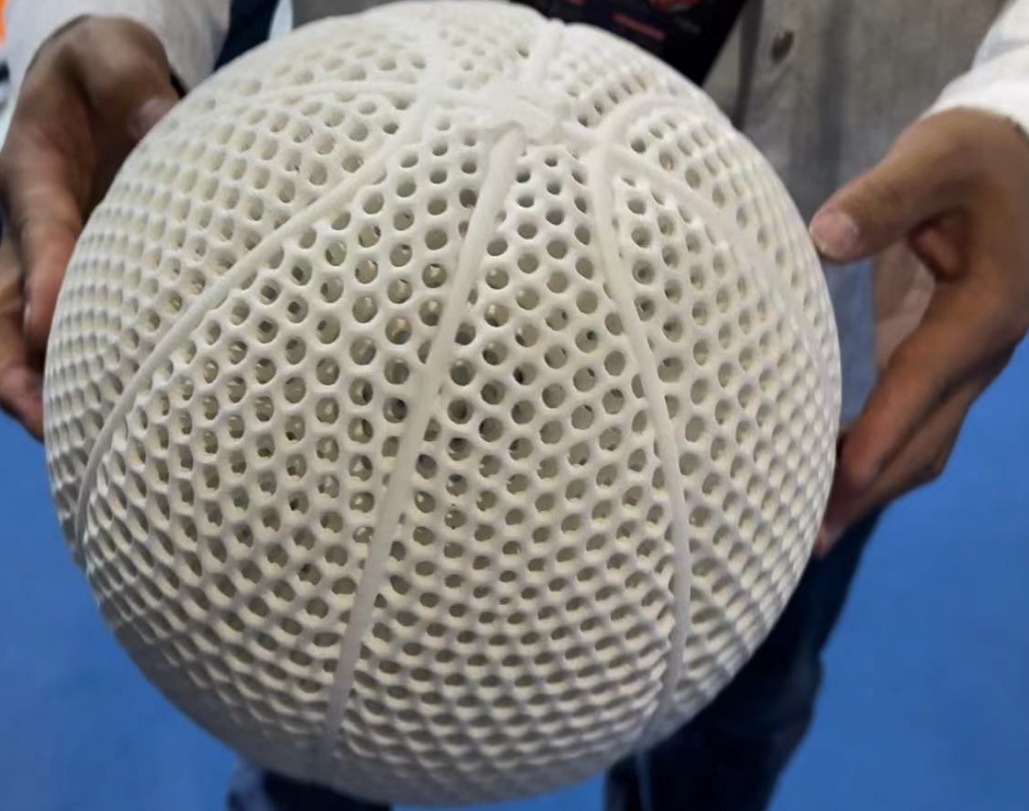
3D printing with TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) opens up a world of possibilities due to its unique properties. TPU is a flexible, durable, and versatile material, making it ideal for creating objects that need to withstand wear and tear while maintaining a certain level of elasticity ghostwriter erfahrungen. This guide will take you through the essential steps and considerations for successfully 3D printing with TPU.
What is TPU?
TPU is a type of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) that combines the best qualities of plastic and rubber. It is known for its high elasticity, abrasion resistance, and ability to withstand impacts. These properties make it suitable for a wide range ghostwriter agentur of applications, from phone cases and shoe soles to automotive parts and wearable technology.
Preparing Your 3D Printer
- Choose the Right 3D Printer
- Nozzle and Bed Temperature
- Bed Surface Preparation
- Cooling Fans
Slicer Settings
- Layer Height
- Print Speed
- Retraction Settings
- Infill and Shells
Printing Process
- Loading the Filament
- First Layer
- Monitoring the Print
- Post-Processing
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Stringing and Oozing
- Poor Layer Adhesion
- Warping
- Filament Jamming