Injection Mold Surface Finishes: VDI vs. SPI
When it comes to injection molding, the surface finish of the mold can significantly impact the final appearance and functionality of the product. Two of the most commonly used standards for specifying mold surface finishes are VDI (Verein Deutscher Ingenieure) and SPI (Society of the Plastics Industry). Understanding the differences between these two standards can help you choose the right finish for your project.
Understanding VDI and SPI Standards in injection molding
What is VDI (Verein Deutscher Ingenieure) surface finish?
The VDI is a German engineering association that has developed various technical standards. The VDI 3400 standard specifies surface roughness for injection molds, ranging from VDI 0 to VDI 45. These numbers correspond to different levels of surface roughness, with lower numbers indicating smoother finishes and higher numbers representing rougher finishes.
– VDI 0-15: Very smooth finishes, typically used for optical parts or high-gloss surfaces.
– VDI 18-30: Medium roughness, suitable for most consumer products.
– VDI 33-45: Rough finishes, often used for industrial parts where appearance is less critical.
VDI Surface Finish Standard Form
VDI Finish | Details | Description | Roughness/µm | Cost |
12 | 600 Stone | Low polish parts | 0.4 | $$ |
15 | 400 Stone | Low polish parts | 0.56 | $$ |
18 | Dry Blast Glass Bead | Satin finish | 0.8 | $$ |
21 | Dry Blast # 240 Oxide | Dull finish | 1.12 | $ |
24 | Dry Blast # 240 Oxide | Dull finish | 1.6 | $ |
27 | Dry Blast # 240 Oxide | Dull finish | 2.24 | $ |
30 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 3.15 | $ |
33 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 4.5 | $ |
36 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 6.3 | $ |
39 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 9 | $ |
42 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 12.5 | $ |
45 | Dry Blast # 24 Oxide | Dull finish | 18 | $ |
What is SPI (Society of the Plastics Industry) surface finish?
The SPI standards are used primarily in the United States and are categorized into four main classes: A, B, C, and D, with subcategories within each class. These standards specify the polishing and texturing processes used to achieve the desired finish.
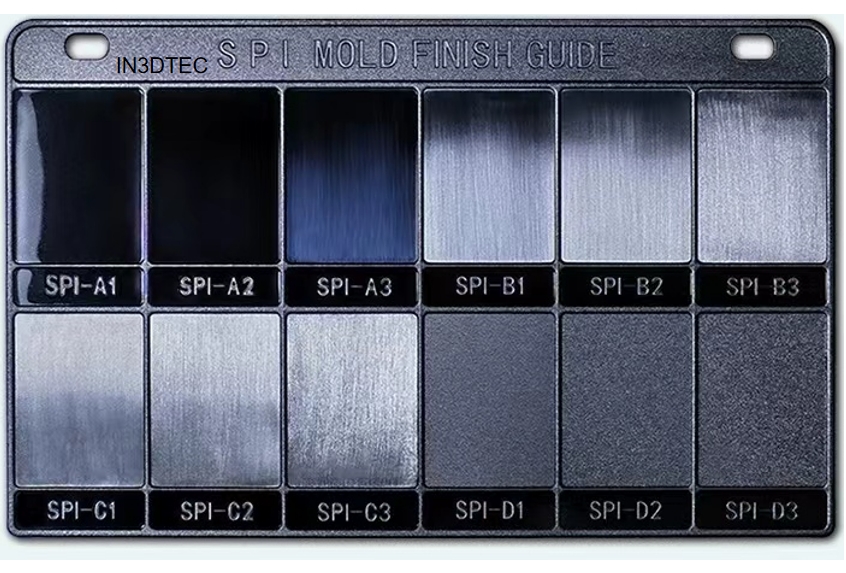

– A-1 to A-3: Mirror finishes achieved through diamond polishing.
– B-1 to B-3: Semi-gloss finishes achieved through grit sanding.
– C-1 to C-3: Matte finishes achieved through stone polishing.
– D-1 to D-3: Textured finishes achieved through various texturing techniques.
SPI Surface Finish Standard Form | |||||
SPI finish | Description | Applications | Roughness (Ra µm) | Suitable materials | Cost |
A-1 | Grade #3, 6000 Grit Diamond Buff | Super Fine polish | 0.012- 0.025 | Acrylic,PC | $$$ |
A-2 | Grade #6, 3000 Grit Diamond Buff | Super Fine polish | 0.025-0.05 | $$$ | |
A-3 | Grade #15, 1200 Grit Diamond Buff | High polish parts | 0.05-0.10 | ABS, Acrylic. PS, Nylon(GF), PC | $$$ |
B-1 | 600 Grit Paper | Medium polish | 0.05-0.10 | ABS, Acrylic, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), PC | $$ |
B-2 | 400 Grit Paper | Medium polish | 0.10- 0.15 | ABS, Acrylic, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), PC | $$ |
B-3 | 320 Grit Paper | Medium polish | 0.28-0.32 | ABS, Acrylic, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), PC | $$ |
C-1 | 600 Stone | Standard polish | 0.35-0.40 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
C-2 | 400 Stone | Standard polish | 0.45-0.55 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
C-3 | 320 Stone | Low polish | 0.63-0.70 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
D-1 | Dry Blast Glass Bead | Satin Surface finish | 0.80-1.00 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
D-2 | Dry Blast #240 Oxide | Dull Surface finish | 1.00-2.80 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
D-3 | Dry Blast #24 Oxide | Dull Surface finish | 3.20-18 | ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PEI, PP. PS, HDPE, Nylon(GF), TPU | $ |
Key Differences Between VDI and SPI Surface Finishes
1. Geographical Use
– VDI: Predominantly used in Europe.
– SPI: Commonly used in the United States.
2. Classification
– VDI: Numeric scale (VDI 0-45).
– SPI: Alphabetic and numeric scale (A-1 to D-3).
3. Surface Finish Range
– VDI: Offers a broad range of finishes from very smooth to very rough.
– SPI: Focuses more on the method used to achieve the finish rather than the roughness level alone.
4. Application Focus
– VDI: Often chosen for its wide range and detailed gradation in roughness levels.
– SPI: Selected based on the polishing and texturing techniques required for the final product.
Choosing the Right Surface Finish Standard for Your Project
When deciding between VDI and SPI standards, consider the following factors:
1. Geographical Preferences: If your manufacturing process or end customers are located in Europe, VDI might be the more familiar standard. Conversely, if your operations are primarily in the U.S., SPI could be more appropriate.
2. Finish Requirements: Determine the specific surface finish you need for your product. If a precise roughness level is critical, VDI’s detailed scale may offer better options. If the method of achieving the finish is more important, SPI’s classification might be more useful.
3. Product Application: Think about the end-use of your product. High-gloss finishes for consumer electronics might benefit from SPI A-class finishes, while industrial components might be well-served by higher VDI numbers.
4. Cost and Time: Consider the cost and time associated with achieving different finishes. Some SPI finishes, particularly those requiring diamond polishing, can be more expensive and time-consuming than comparable VDI finishes.
If you want to purchase the VDI or SPI card sample, please contact [email protected]
Conclusion
Both VDI and SPI standards provide valuable frameworks for specifying injection mold surface finishes. By understanding the differences and considering the specific needs of your project, you can make an informed decision that ensures the best quality and performance for your molded products. Whether you prioritize the method of finish or the level of roughness, choosing the right standard is crucial for achieving the desired results in your injection molding processes.