Overmolding vs. Insert Molding What’s the difference?
What Is Overmolding?
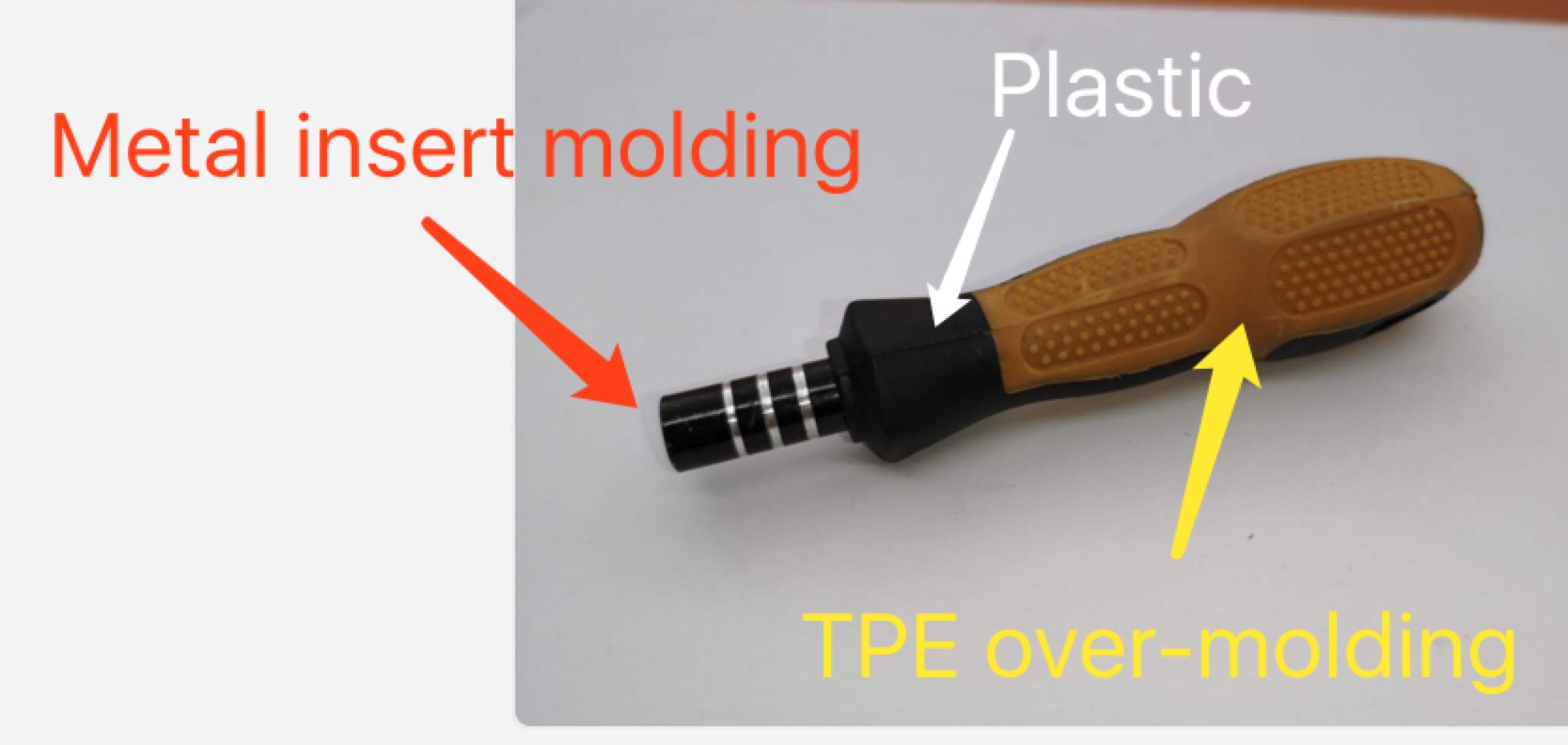
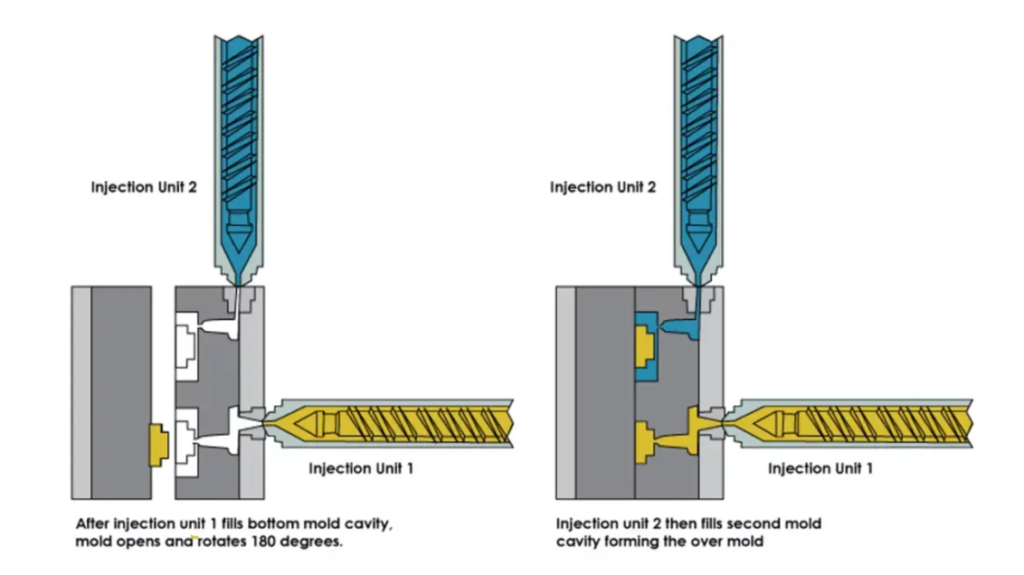
Overmolding is a multi-step injection molding process where two or more components are molded over top of one another. Overmolding is sometimes referred to as two-shot molding because it is a two-step process.
First, a base component (otherwise known as a substrate) is molded and allowed to cure. Overmolded substrates are often made of plastic. Then, a second layer is molded directly on top of the first to create a single solid piece. Overmolding is commonly used to manufacture plastic parts that feature a rubber handle. The two-shot process of overmolding a toothbrush, for example, consists of forming a base layer for the plastic handle and a top layer of rubber (to make the toothbrush less slippery to hold).
|
|
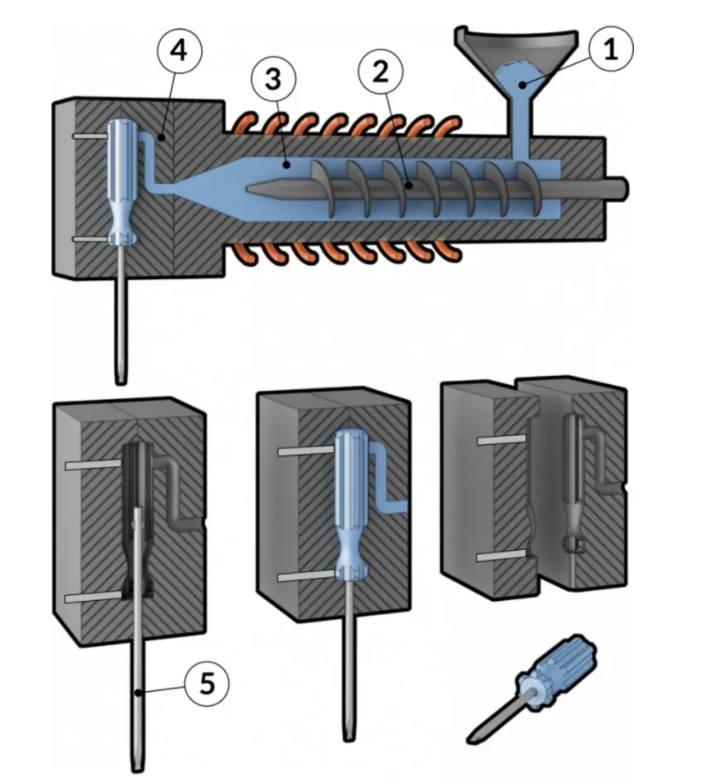
Why Choose Insert Molding?
Insert molding is a versatile process that has numerous benefits, some of which are listed below.
- Reduced Assembly Cost – An injection molding machine can create thousands of parts per day. Such economies of scale can significantly reduce the cost of the individual parts. In a typical CNC machined, sheet metal, or additive manufactured part, any required assembly can be a major bottleneck. Insert molding can be used to eliminate assembly and thus maximize cost savings.
- Part Performance – In general, plastic parts are less robust than their metal counterparts. However, plastic offers other benefits such as reduced cost, superior design flexibility, and lighter weight. Combining both metal and plastic materials into one part can capitalize on the benefits of both. Metal inserts can be used where strength and stiffness are required and the remainder of the part can be made of plastic to reduce weight. Moreover, plastic parts do not fare well against wear and tear and metal inserts add an element of durability to parts to withstand any kind of cyclical loading.